
Algorithmic trading based on orderbook: basic principles
Much attention in trading is paid to algorithmic trading, but few people know and use strategies based on Orderbook for automation, and we will tell you more about it.
What is Orderbook and how it works
Orderbook is a tool that reflects in real time the current limit orders to buy and sell an asset. It is also called a price book or order book. It allows market participants to see what volumes are ready to buy or sell and at what prices. In the context of the cryptocurrency market, the cryptocurrency orderbook serves as the most important source of information for a trader, especially when using algorithmic strategies. It is updated every second in response to new orders and changes to existing ones, forming a dynamic picture of supply and demand on the exchange.
Through the orderbook you can assess the state of the market: activity, interest in a particular asset, as well as likely price movements. By analyzing its structure, traders and algorithms get an idea about the behavior of other participants and can make more accurate trading decisions.
Orderbook structure: ask, bid, spread
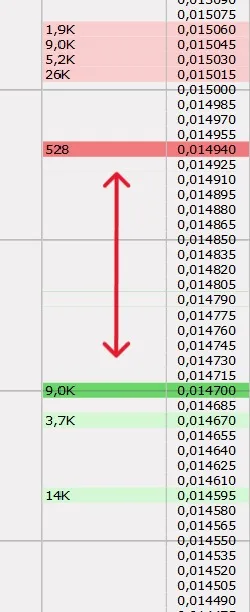
The Orderbook consists of two parts - bid and ask. Bid levels represent limit buy orders. These are the prices at which participants want to buy the asset. The higher the price in this list, the closer it is to the market price and the higher the chances that the order will be executed. Ask levels, on the other hand, are selling prices at which traders are willing to sell the asset. The lowest price in the ask and the highest price in the bid form what is known as the bid ask spread - the difference between the best bid price and the best ask price.
Bid ask spread is not just a technical term. It plays an important role in understanding current market liquidity. A narrow spread indicates high trading activity and tight competition between orders. A wide spread can indicate low liquidity, increased risk and possible slippage in order execution.
Visually, the orderbook is often presented as a table or chart, where each row reflects the price level and the volume of orders at that level. The highest in the bid part and the lowest in the ask part is the current market price, at which trades are executed in the moment.
Liquidity and market depth
Liquidity is the ability of an asset to be bought or sold quickly without significantly affecting its price. In the context of an orderbook, this means having a large number of orders at different price levels.
Orderbook depth is a measure of liquidity, showing how much volume is concentrated at each price level on both sides - bid and ask.
The more bids and the more evenly they are distributed across the levels, the higher the depth and the more stable the price behavior at high trading volumes. If the depth is insufficient, a large order can “eat” several levels at once, causing a sharp price jump - this is called slippage.
Orderbook depth is especially important for large players, market makers and algorithms that use staking or order trading algorithms. Such strategies rely on not only taking into account current orders, but also analyzing changes in their distribution. For example, the sudden appearance of a large order can signal a potential market reversal or an attempt to manipulate the market.
The presence of market makers - participants who provide liquidity by constantly placing buy and sell orders - has a positive effect on the depth of the orderbook. They smooth out price fluctuations and make the market more predictable. That is why platforms with advanced algorithmic trading systems, such as Veles Finance, take these parameters into account in their strategies and offer tools to analyze them.
Fundamentals of algorithmic trading
When diving into the process of trading automation, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with the basics of algorithmic trading and choose the right software (trading bots).
Algorithms and trading signals
Algorithmic trading is a method of automated trading, in which the decision to enter and exit transactions is made not by a human, but by a trading program based on predetermined rules. Such systems analyze market data in real time, track the behavior of prices, volumes, changes in the price stack, and make transactions instantly, without trader’s participation.
The basis of any algorithm is trading signals. These are triggers that activate a specific action. For example, buying an asset when a specified condition is met. Signals can be formed on the basis of technical indicators, data from the orderbook, changes in the depth of the orderbook, as well as analysis of the order flow or the behavior of market makers.
Veles Finance provides users with the ability to trade using ready-made algorithms, which makes algorithmic trading accessible even to beginners. Users can run already tested strategies without having to write code or understand complex logic. These algorithms take into account the behavior of limit orders, volume distribution, strength of buyers and sellers, and other signals from the order book.
In addition, the platform has a marketplace where you can select and copy working strategies developed by experienced traders. This simplifies the way to automated trading. All you need is to select a strategy, customize the parameters and put it to work. The user gets access to monitoring and management tools, and can optimize the strategy using the built-in functionality for testing on historical data - backtests.
Speed of execution and the role of latency
Speed is also one of the success factors in algorithmic trading, especially in the context of strategies related to staking trading and order flow analysis. Even a minimal delay between signal arrival and trade execution can affect the outcome, especially in high volatility or high-frequency trading.
Veles Finance platform takes this into account and offers a technology infrastructure with minimal delays. The algorithms running on the platform process signals in real time and perform actions without delays critical for fast-acting strategies. This is especially important when analyzing market microstructure, where milliseconds count, and the slightest delay can lead to reduced efficiency.
Algorithms using orderbook data
Strategies based on orderbook data analyze orders, depth and behavior of other participants. They are able to detect anomalies in volume distribution, sudden changes in order flow, and the actions of market makers.
They also use cluster analysis - a tool that allows estimating the concentration of volumes and possible price reversal points. All this helps to create an accurate and adaptive algorithm of order trading.
Limitations and risks of such strategies
Despite the high potential, trading by stack comes with certain risks. Manipulation (e.g. spoofing), false signals and high volatility can affect the accuracy of the algorithm. It is also important to consider commissions, especially when the frequency of trades is high. Therefore, risk management and fine-tuning of strategies are prerequisites for stable trading.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between stack and orderbook depth?
The stack shows current orders, while the depth shows volumes at each level.
2. Can I use algorithms without experience?
Yes, Veles Finance offers ready-made solutions that do not require deep knowledge.
3. What is order flow and why do I need it?
It is an order flow that helps to understand the balance of power between buyers and sellers.
4. What are the risks of trading on the glass?
Manipulation, sudden market movements, false signals and commissions.
5. Is the platform suitable for professionals?
Yes. Support for flexible settings, high-speed execution and powerful analytical tools allow you to implement even the most complex strategies.
