
How cryptocurrency was invented
People around the world are already using cryptocurrency or are just starting to do so. However, not everyone knows how the technology that has forever changed the financial system came about.
How cryptocurrency came about and its significance
To understand how cryptocurrency came about, we need to look back to the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Even then, there was active discussion around the world about the idea of creating digital money that could exist without control by the state or banks. People were looking for a way to transfer value directly to each other via the Internet, without intermediaries, bureaucracy, or high commissions. There were attempts to create similar projects, such as DigiCash and e-gold, but they all depended on centralized companies and eventually ceased to exist.
The real breakthrough came in 2008, when an unknown programmer under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” It described who invented Bitcoin and what it was all about. He proposed blockchain technology, which allowed transactions to be stored and verified in a distributed network, eliminating the possibility of counterfeiting and double spending. In 2009, the first block, Genesis Block, was launched, and the world saw the first cryptocurrency.
The point of Bitcoin and subsequent digital assets was to give people the freedom to manage their finances. Unlike the traditional banking system, where funds are controlled by a third party, cryptocurrency provides independence and decentralization. It creates a financial system where trust is built not on laws or banks, but on mathematics and cryptography.
In essence, the history of cryptocurrencies began as a response to the crisis of confidence in traditional institutions. Whereas money used to be completely dependent on the state, there is now an alternative — a system that works thanks to network participants around the world. It is this system that became the foundation for the further development of blockchain and the beginning of the global evolution of cryptocurrencies. After all, they were originally conceived not just as a means of payment, but as a new stage in the history of finance and technology.
Bitcoin White Paper
The Bitcoin White Paper is the document that started the whole history of Bitcoin and cryptocurrency in general. It was published in 2008 by a person or group of people under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It described in detail how cryptocurrency came about, how a decentralized system should work, and why it could become an alternative to traditional finance.

Abstract of the Bitcoin White Paper Bitcoin.org
Satoshi proposed creating a network where transactions are recorded in a chain of blocks and verified by participants without the involvement of banks or the state. The document explained that protection is provided by cryptography and the Proof-of-Work algorithm, and the issuance of coins is strictly limited, which makes Bitcoin independent of inflation. Thus, the white paper became a kind of constitution for the first cryptocurrency. It not only showed the world a new type of digital money, but also set the direction for the future development of blockchain and evolution of cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum and other projects.
How the first blockchain worked
When Satoshi Nakamoto launched the first cryptocurrency in January 2009, the technology behind it, blockchain, also appeared. To understand how cryptocurrency came about, it is important to understand how its foundation worked.
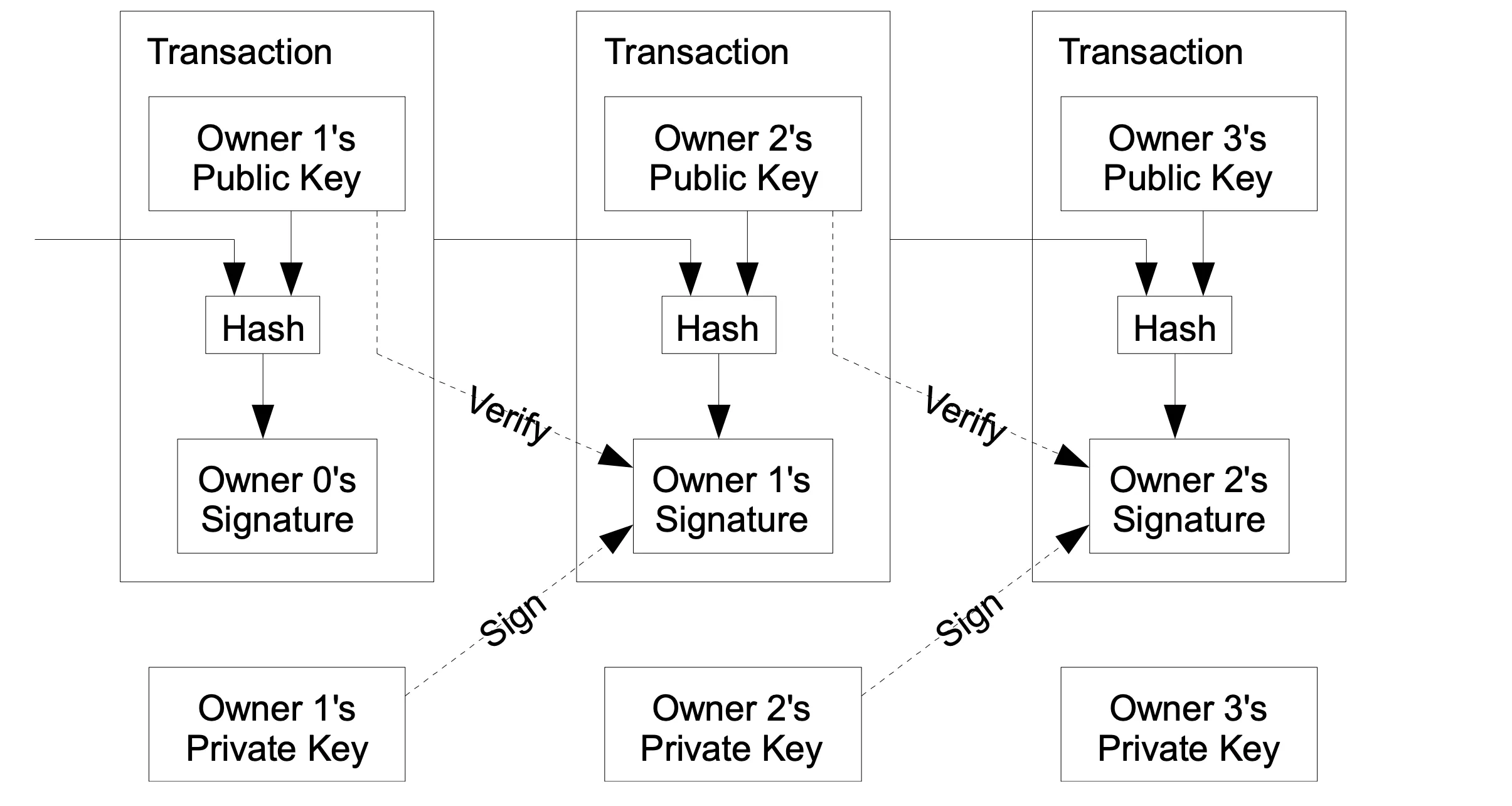
Transactions Bitcoin.org
The first blockchain was a distributed database where all transactions were recorded in blocks. These blocks were linked together in a chronological chain, forming a single ledger. Each new block contained a link to the previous one, which made the system virtually impossible to fake. In other words, to change one entry, you would have to rewrite the entire chain at once, which seemed impossible in a distributed network of thousands of computers.
The launch began with the Genesis Block, a zero block that Satoshi created manually. In it, he left a symbolic record: the headline of an article from the British newspaper The Times about the 2008 banking crisis. This became a kind of manifesto against financial instability and a signal of why digital money is needed.
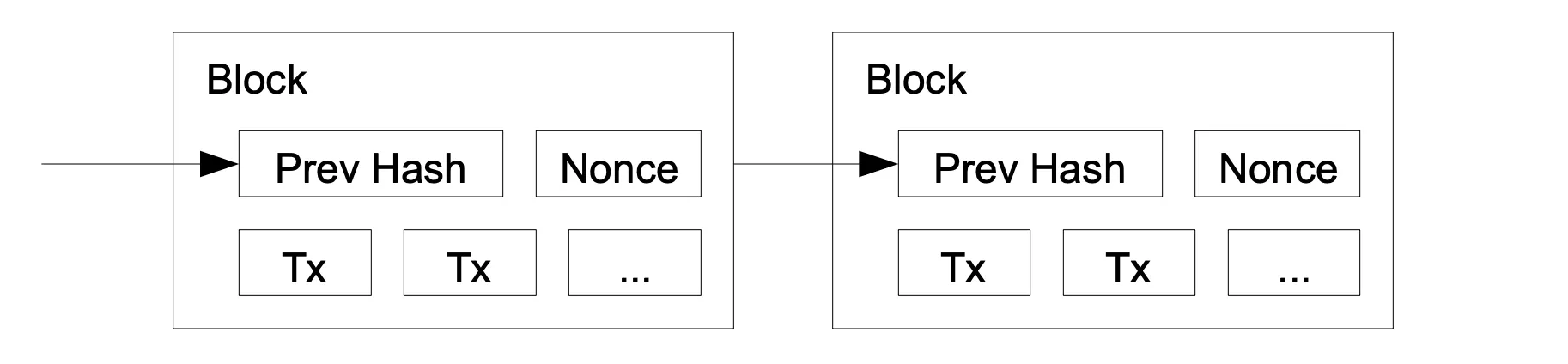
Proof-of-Work algorithm Bitcoin.org
The blockchain’s mechanism was built on consensus — an agreement among network participants about what information is correct. In Bitcoin, this was ensured by the Proof-of-Work algorithm. Mining computers solved complex mathematical problems to add a new block to the chain. For this, they received a reward in the form of new coins. This is how the first Bitcoins appeared, and this became the starting point for all cryptocurrencies. Each transaction in the blockchain was signed using cryptography, which guaranteed its authenticity. No one could spend the same coin twice, as the network checked all transactions and recorded them in the registry. Thanks to this, Bitcoin became a truly reliable system that did not depend on banks or states.
The development of blockchain began with a simple but ingenious idea: to combine cryptography, distributed networks, and a reward mechanism. It was in this form that it ensured decentralization and became the basis for the further evolution of cryptocurrencies. The path from the first blocks to modern decentralized applications was quite long. However, the Genesis Block and the early years of Bitcoin laid the foundation for what is now called the digital economy of the future.
When altcoins appeared
People saw the potential of cryptocurrency as an independent financial system. It became clear that blockchain technology opened up far more possibilities than just digital transfers. Bitcoin became the first cryptocurrency, but soon projects appeared that attempted to develop its ideas or offer alternative solutions. These were called altcoins, meaning “alternative coins.” The first altcoins began to appear in 2011, just two years after the launch of Bitcoin.
One of the first was Namecoin, which used blockchain not only for financial transactions but also for decentralized domain name registration. The project demonstrated that in the development of blockchain, the possibilities of the technology could go beyond money. In the same year, the well-known Litecoin appeared — a cryptocurrency created as “digital silver” in relation to Bitcoin. It offered faster transactions and a different emission model. Litecoin became one of the most successful projects of that time and proved that altcoins could find their niche.

Later, dozens and hundreds of new projects began to appear, many of which offered unique ideas: increased anonymity (Dash, Monero), improved scalability, or specialized functions. However, the real turning point was the story of Ethereum. When Vitalik Buterin proposed a platform for smart contracts, cryptocurrencies ceased to be just a means of payment. It was Ethereum that paved the way for the creation of decentralized applications (dApps), which marked the beginning of a new era in the industry.
After Bitcoin, cryptocurrency took the path of diversity. Altcoins became a kind of laboratory of ideas, where different models and technologies were tested. Some projects disappeared as quickly as they appeared, while others changed the market forever and remain leaders to this day. The evolution of cryptocurrencies is largely linked to altcoins, which transformed blockchain from a tool for digital money into a global platform for innovation. Today, altcoins occupy a significant part of the market, forming entire ecosystems and offering solutions for finance, logistics, medicine, and public administration. Their emergence was an inevitable step after Bitcoin and proved that the idea of decentralization can be applied in many different areas of our lives.
How cryptocurrency affects the economy
Now, the history of cryptocurrencies has gone far beyond enthusiasts and technical experiments. More and more educational materials in the form of books and films are being devoted to this asset class. Bitcoin and its followers have become a full-fledged financial instrument that influences the global economy. To understand this effect, we need to consider several key areas in which digital assets have changed the usual rules.
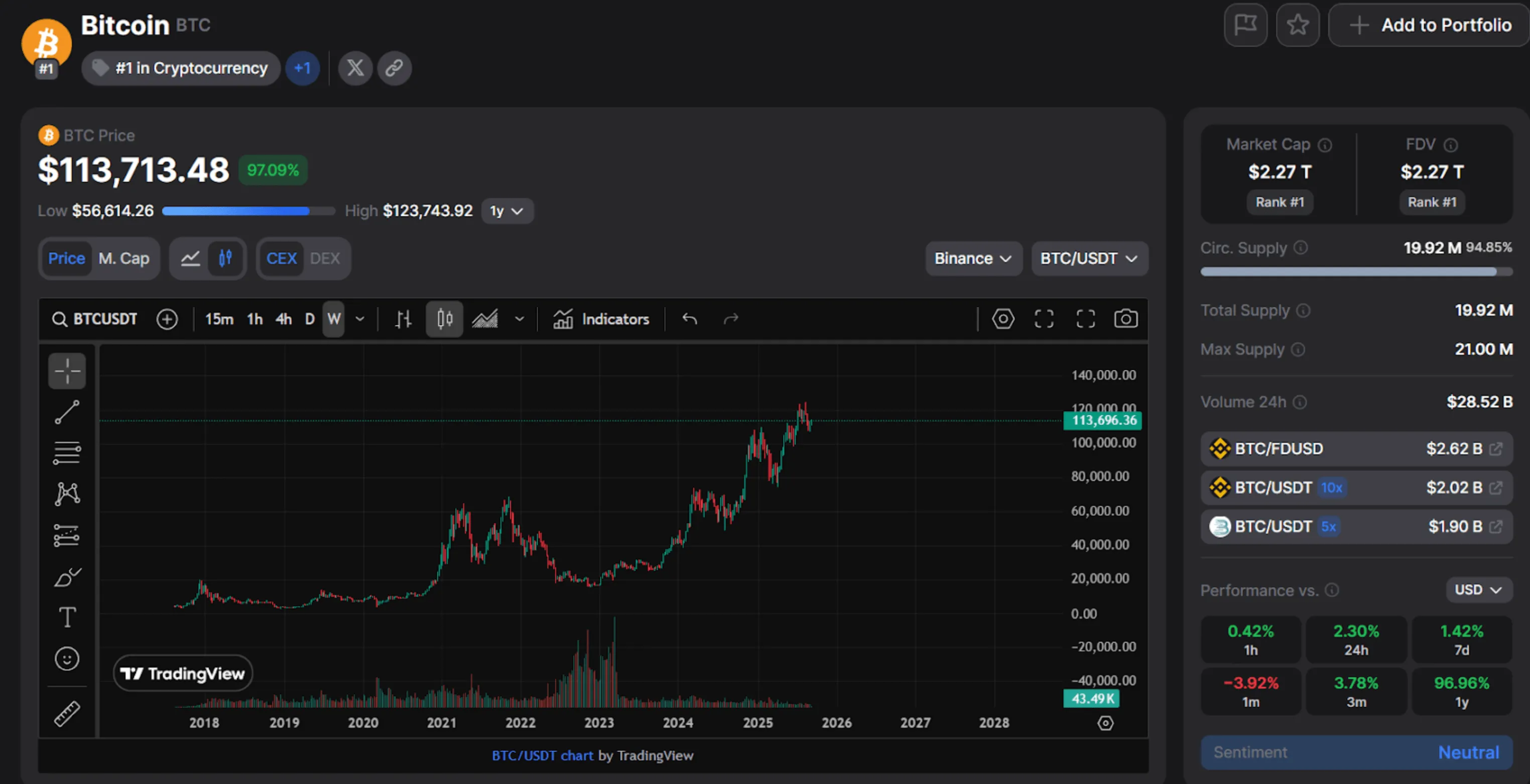
First of all, cryptocurrency has become a new form of money. It has proven that digital money can exist without central banks, and transactions can take place directly between people, regardless of borders. This has facilitated international settlements and reduced transfer costs. In countries with high inflation and economic instability, people use cryptocurrencies as a means of preserving capital, making them an alternative to gold and the dollar.
Second, cryptocurrencies have changed the investment landscape. Millions of private investors have emerged who have gained access to high-yield assets for the first time. Large funds and corporations have also begun to invest in Bitcoin, recognizing it as “digital gold.” All of this has significantly strengthened the status of cryptocurrencies in the global financial system and made them part of the long-term strategy of many companies.
Blockchain technology has also become an important element. The development of blockchain has influenced the economy not only through cryptocurrencies, but also through the introduction of decentralized applications and smart contracts. These solutions reduce management costs, eliminate corruption, and create transparency. That is why many states and corporations view blockchain as a tool for modernizing the economy.
In addition, cryptocurrencies have changed the approach to startups and financing. ICOs and subsequent forms of tokenization have allowed companies to raise millions of dollars without traditional banks and stock exchanges. This approach has given impetus to innovation, but it has also created risks of fraud, which has become part of the complex evolution of cryptocurrencies.
However, the impact of cryptocurrencies on the economy is not always positive. Market volatility can cause financial turmoil, and governments are concerned about the possibility of cryptocurrencies being used to circumvent sanctions and for shadow operations. These factors are forcing states to actively study regulatory issues and seek a balance between innovation and control.
The history of Bitcoin and many other digital assets shows that cryptocurrency has already become an integral part of the global economy. It influences capital flows, investments, international transfers, and technological development. In the future, its role will only grow stronger, and the evolution of cryptocurrencies will continue to change the financial world, making it more decentralized and technologically advanced.
FAQ
1. Who invented Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was created by Satoshi Nakamoto, whose identity remains unknown to this day.
2. When did Bitcoin appear?
The first cryptocurrency appeared in January 2009 with the launch of Genesis Block.
3. What is the point of cryptocurrency?
Its main goal is to create decentralized digital money that is independent of banks and the state.
4. How did blockchain develop?
The development of blockchain began with Bitcoin and then continued with Ethereum and other projects.
5. What does the evolution of cryptocurrencies mean?
It is the process of transitioning from a simple payment system to a complex ecosystem using smart contracts and decentralized applications.
