
What is farming in cryptocurrency
In traditional finance, there are options for investing capital at interest. In cryptocurrency, a similar way for investors to earn interest is through farming.
What is farming in simple terms
To explain it as simply as possible, farming in crypto is a way to earn income from your cryptocurrency assets without selling them. In essence, it’s like a bank deposit, except in the world of DeFi farming, it happens through liquidity poolsand smart contracts. Users temporarily transfer their coins to a platform, which uses them for trading or lending and pays a reward in return.
At the same time, beginners confuse the terms phishing and farming: the first is associated with cyberattacks, and the second is an honest way to earn money in decentralized finance.
How farming works in cryptocurrency
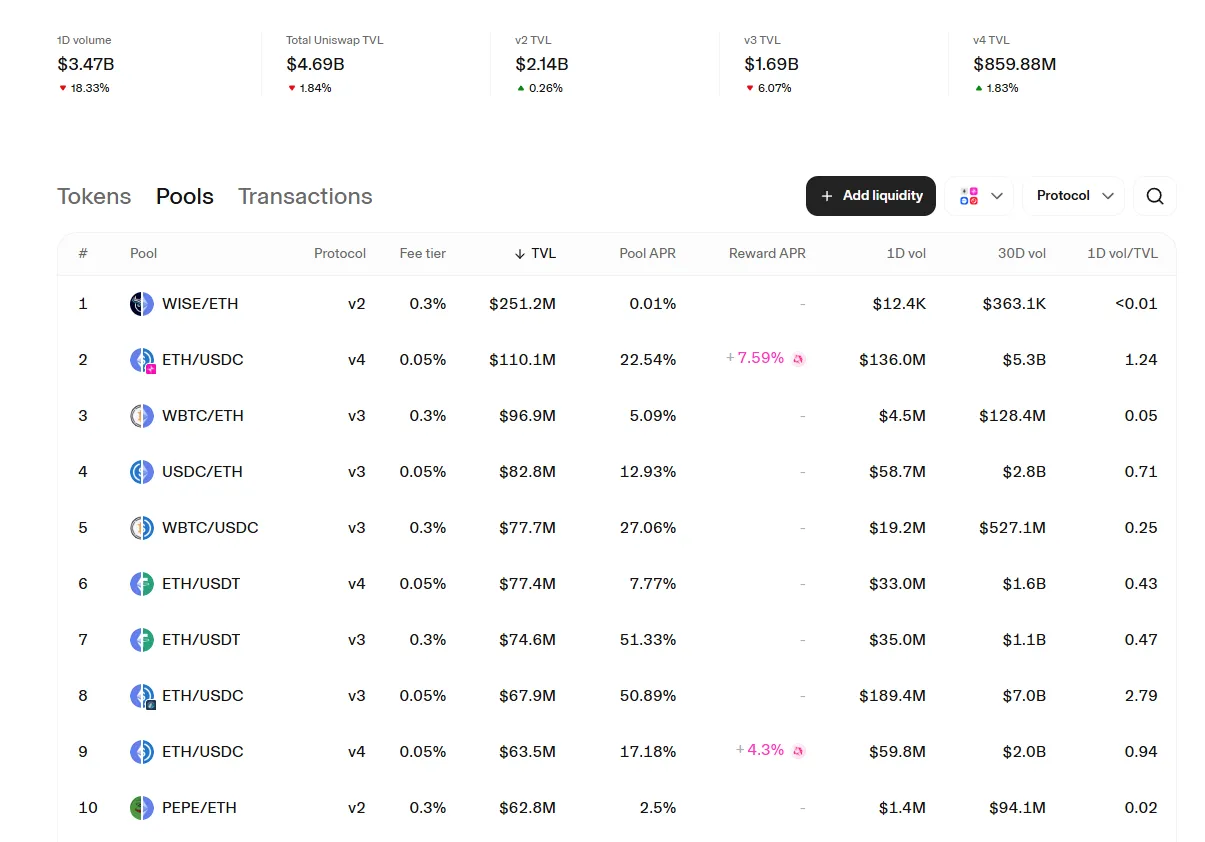
The mechanism of yield farming is simple: you add cryptocurrency to cryptocurrency liquidity pools, which decentralized exchanges need to operate. In return, you receive a percentage of user fees or special reward tokens.
For example, Uniswap liquidity pools allow tokens to be traded directly between users without intermediaries. To create a liquidity pool, you need to deposit an equal value of two tokens (for example, ETH and USDT) and sign a smart contract. However, it is important to remember the risk of impermanent loss — a temporary loss in asset value due to price fluctuations.
Types of farming in crypto
There are several popular formats in the cryptocurrency space:
- Liquidity mining — providing liquidity to an exchange and receiving rewards in the form of project tokens.
- Yield farming — investing in different pools and platforms to maximize income.
- Staking — freezing coins on the network to confirm transactions and receive rewards. Each method has a different level of profitability and risk.
Popular platforms for cryptocurrency farming
Today, there are many platforms for cryptocurrency farming, but the most famous ones are: farming on PancakeSwap— a Binance Smart Chain platform with low fees, farming on Uniswap — one of the first DEXs to launch mass liquidity pools, as well as Curve, Aave, and Balancer projects aimed at experienced users.
How to start farming cryptocurrency
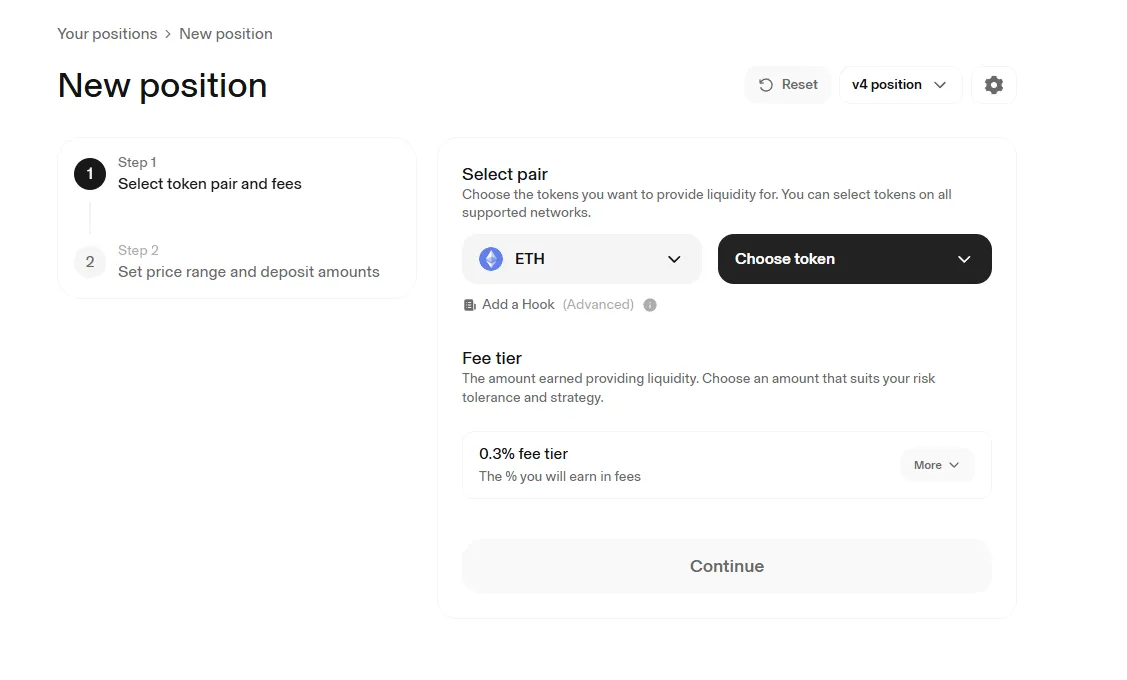
To understand what it means to farm crypto, you can follow a simple path:
- Choose a platform (PancakeSwap, Uniswap, Aave, etc.).
- Create a crypto wallet (for example, MetaMask).
- Buy or transfer the necessary tokens.
- Create a liquidity pool or join an existing one.
Monitor returns and risks (impermanent loss, smart contract hacks).
Beginner mistakes in farming
Even when they understand what crypto farming means, many beginners make typical mistakes that can lead to capital loss. One of the most common mistakes is investing in questionable projects without prior verification. In the field of DeFi farming, fraudulent pools or fake copies of well-known platforms are common, and investors attracted by high returns risk losing all their investments. To avoid this, it is important to check the reputation of the project, study reviews, the team, and the availability of smart contract audits.
Another serious problem is ignoring the risk of impermanent loss (losses due to asset volatility). When participating in a cryptocurrency liquidity pool, the price of one of the tokens may change so that the final amount upon withdrawal is less than with conventional asset storage. This has a very painful effect when volatility is high. To reduce risk, experienced traders advise starting with stablecoin pairs, such as USDT/USDC, where price fluctuations are minimal.
Often, beginners choose the wrong platform, preferring little-known DEXs with the promise of super profits, ignoring proven options such as PancakeSwap or Uniswap.
Such a choice can result in the loss of funds due to hacking/scam or sudden closure of the platform.
The lack of diversification is also dangerous. By investing all of their capital in one pool or on one platform, users expose themselves to the risk of losing everything in the event of a smart contract failure or a sharp change in asset prices. A more reliable approach is to distribute funds across several pools, tokens, and platforms.
Many also underestimate the impact of fees and taxes. In high-traffic networks, such as Ethereum, transaction fees can eat up a significant portion of your income. In addition, in some countries, income from cryptocurrency farming is taxed, which is also worth considering in your calculations. To minimize costs, it is better to choose networks with low fees, such as Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, or Arbitrum, and clarify tax obligations in advance.
FAQ
1. What is farming in simple terms?
It is a way to earn money on cryptocurrency by providing it to liquidity pools for the operation of decentralized platforms.
2. What does it mean to farm crypto?
It means investing your tokens in DeFi projects and receiving rewards.
3. How does yield farming differ from liquidity mining?
Liquidity mining is providing liquidity to a platform and receiving rewards, while yield farming involves a set of strategies to maximize income by lending assets.
4. What are the risks of farming?
The main ones are losses due to exchange rate volatility, smart contract hacks, and market volatility.
5. Can you start with a small amount?
Yes, but commissions and risks can eat up a significant portion of your profits.
